FELINE NEONATAL COINFECTION OF TOXOPLASMOSIS AND CYSTOISOSPOROSIS – CASE REPORT
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21708/avb.2018.12.2.7635Resumo
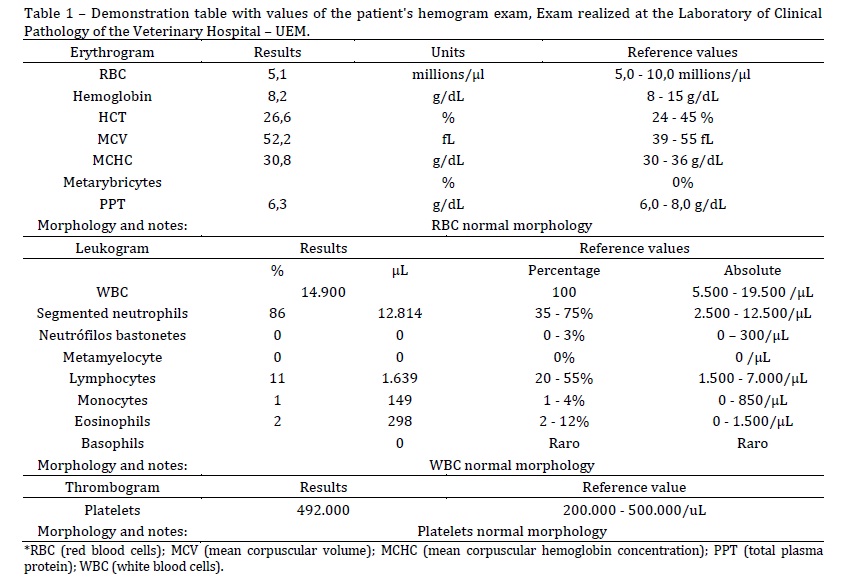
Toxoplasma gondii and Cystoisopora spp. are coccidian protozoa and compulsory intracellular parasites. These parasites present an enteric cycle phase, wild and domestic felines are definitive hosts capable of eliminating non-sporulated oocysts by faeces. Furthermore, they share the same transmission path, through the ingestion of infectious oocysts or the ingestion of cysts present on tissues. Most cat infections occur subclinically. Commonly, clinical and severe disease develops more often in kittens and immunocompromised animals. The present paper reports a case of coinfection of T. gondii and Cystoisospora spp in a feline of approximately 20 days old, weighing 260 grams, assisted at the Veterinary Hospital - UEM. The patient presented acute signs of limited mobility, remaining only in sternal position, cervical ventroflexion, dyspnea, lethargy and anorexia. T. gondii was identified through Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) test using a blood sample, whereas the co-analysis by flotation in saturated saline solution (Willis technique) was able to verify the presence of oocysts of Cystoisospora spp. After negative result from PCR test using stool sample, the presence of Cystoisospora spp. was confirmed, differentiating it from oocysts of T. gondii. The treatment based on sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim was able to control the infection and decrease disease symptoms, proving to be effective and showing significant clinical improvement within 3 days after starting the treatment.
Downloads
Downloads
Publicado
Edição
Seção
Licença
Autores que publicam na Acta Veterinaria Brasilica concordam com os seguintes termos: a) Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. b) Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. c) Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).


 Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença
Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença 