Evaluation of two DNA extraction techniques in the detection of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae by PCR in lungs samples of pigs with and without pneumonia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21708/avb.2019.13.4.8532Resumo
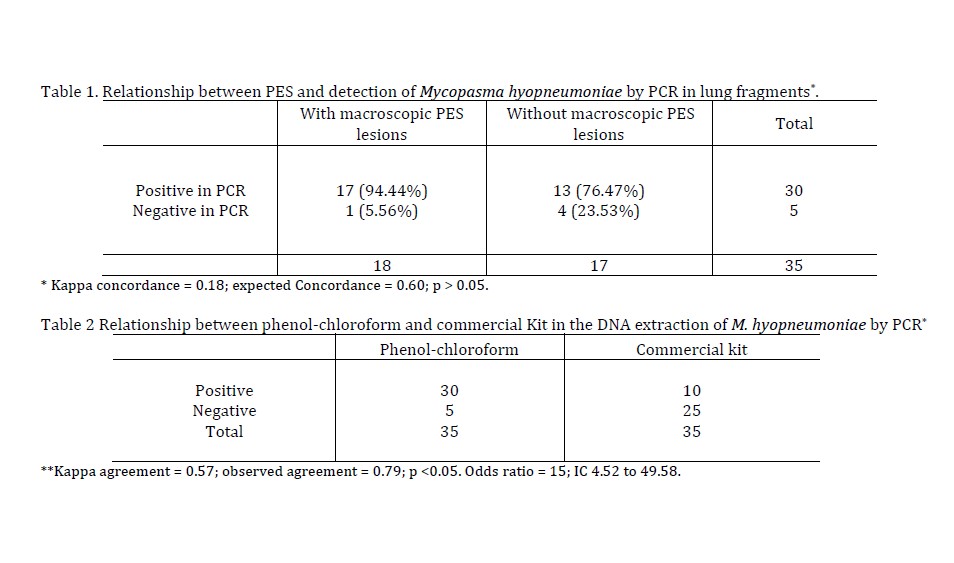
Swine Enzootic Pneumonia (PES) has as the primary etiologic agent the Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. The diagnosis of PES involves clinical manifestations on farms, macroscopic lesions visualized in the slaughterhouse and laboratory techniques, such as isolation by culture, histopathology, immunohistochemistry, ELISA and other serological tests and PCR. This work aimed to establish the comparison between PCR results and typical macroscopic findings in lungs with PES and to evaluate the efficacy of PCR results with extraction by phenol-chloroform and commercial kit in fragments of swine lungs. The efficacy of PCR was evaluated by comparing the classic method of DNA extraction by phenol-chloroform and by commercial Kit. Fragments of lungs of 18 pigs with characteristic lesions of PES and 17 without lesions were subjected to DNA extraction and posterior PCR. The pulmonary lesions with PES were PCR-positive in 94.44%, compared to 76.47% of the non-PES lungs. Kappa concordance between macroscopic and PCR was 18%, which was not significant (P > 0.05). Of the 35 lung fragments processed by phenol-chloroform, 85.71% were positive by PCR, compared to 28.57% by the commercial kit. Kappa agreement between DNA extraction methods was 57%, which was statistically significant (p <0.05), but Odds ratio was 15 (CI 4.52 to 49.68), which means that the probability of PCR positivity by the phenol-chloroform method was 15 times higher than that by the commercial kit. Macroscopy and PCR results were discordant, with phenol-chloroform extraction being the best between both procedures.
Downloads
Downloads
Publicado
Edição
Seção
Licença
Autores que publicam na Acta Veterinaria Brasilica concordam com os seguintes termos: a) Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. b) Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. c) Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).


 Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença
Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença 