Seroprevalence and risk factors for Neospora caninum infection in dogs of rural areas of the Brazilian Semi-arid Region
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21708/avb.2020.14.1.8936Resumo
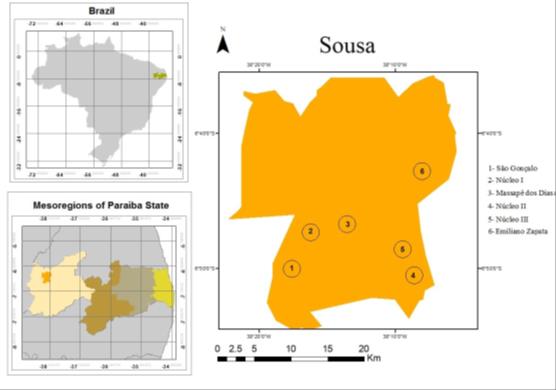
Neospora caninum is a protozoan of the heteroxenous cycle, whose definitive hosts include domestic and wild canids, while intermediate hosts are herbivores. Its occurrence in dogs of rural areas deserves attention due to the risk of transmission to the animals of production, mainly cattle. The objective of this study was to determine the prevalence of N. caninum antibodies in dogs belonging to rural areas of the municipality of Sousa, the semi-arid region of Paraíba, Northeastern Brazil. Blood sera from dogs of six rural communities were analyzed. The indirect fluorescent antibody test was performed for the detection of anti-N. caninum IgG. The results were considered positive when the total peripheral fluorescence of the tachyzoites occurred at a dilution ≥1:50. The frequency of seropositivity was 9.18% (9/98 cases). Antibody titers ranged from to 200, with the 1:50 titer being predominant. Among the evaluated sites, 66.6% (4/6) showed the presence of at least one seropositive dog. The variable contact with cattle was considered a risk factor (odds ratio = 15.25) for infection by the parasite, demonstrating a higher risk of contact with contaminated tissues. It was concluded that dogs from rural areas of the municipality of Sousa were exposed to N. caninum, and it was suggested that contact between dogs and cattle be avoided as a control measure to prevent infection in dogs.
Downloads
Downloads
Publicado
Edição
Seção
Licença
Autores que publicam na Acta Veterinaria Brasilica concordam com os seguintes termos: a) Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. b) Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. c) Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).


 Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença
Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença 