Brucellosis and bovine tuberculosis in dairy farms in the state of Acre, Brazil
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21708/avb.2021.15.2.9663Resumo
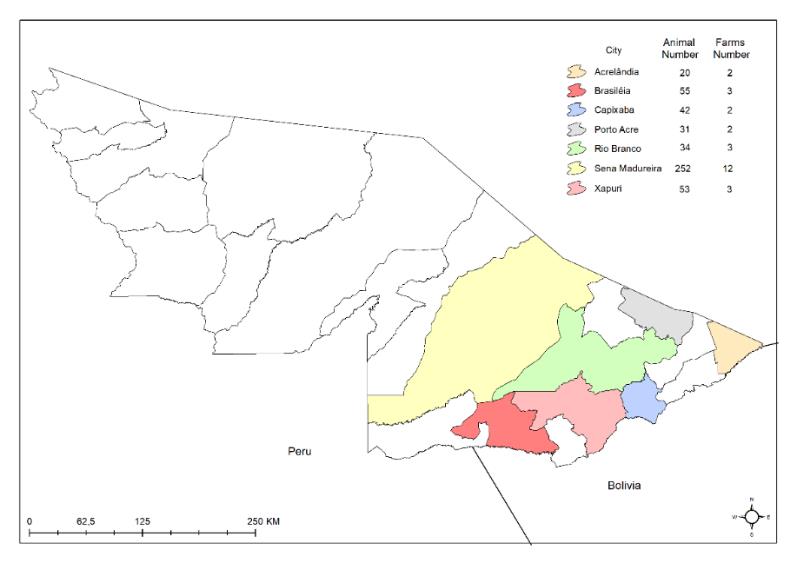
This study aimed to evaluate the to evaluate the occurrence rate of bovine brucellosis and tuberculosis in dairy herds of Acre State, Brazil. The survey was performed on 487 lactating cows distributed across 27 farms in seven cities from June 2018 to February 2019. Farms were selected according to the following criteria: volume of milk production (150 L/day), distance to an urban perimeter (43 km), and time of dairy activity (12 years). For the diagnosis of brucellosis, buffered acidified plate antigen (BAPA) and complement fixation (CF) tests were used. Among the investigated animals, the occurrence rates for brucellosis and tuberculosis were 1.88% (9/487) and 1.23% (6/487), respectively; among the investigated farms, 11.11% (3/27) and 22.2% (6/27) had livestock diagnosed as positive for brucellosis and tuberculosis, respectively. The farms with tuberculosis-positive cattle possessed some common features with respect to herd size. These farms had considerable herd sizes, which were reared extensively in pastures shared with other susceptible or pathogen-carrying animals. In conclusion, the occurrence rate of bovine brucellosis and tuberculosis in dairy herds from Acre state is, in general, lower than that observed in other states of Brazil. Nevertheless, there is an urgent need for developing strategies to control and eradicate both diseases to prevent eventual outbreaks and pathogen dissemination.
Downloads
Downloads
Publicado
Edição
Seção
Licença
Autores que publicam na Acta Veterinaria Brasilica concordam com os seguintes termos: a) Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. b) Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. c) Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).


 Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença
Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença 