Detection of Pseudomonas sp. in pirarucu (Arapaima gigas): a case report in the Western Amazon
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21708/avb.2020.14.4.9204Abstract
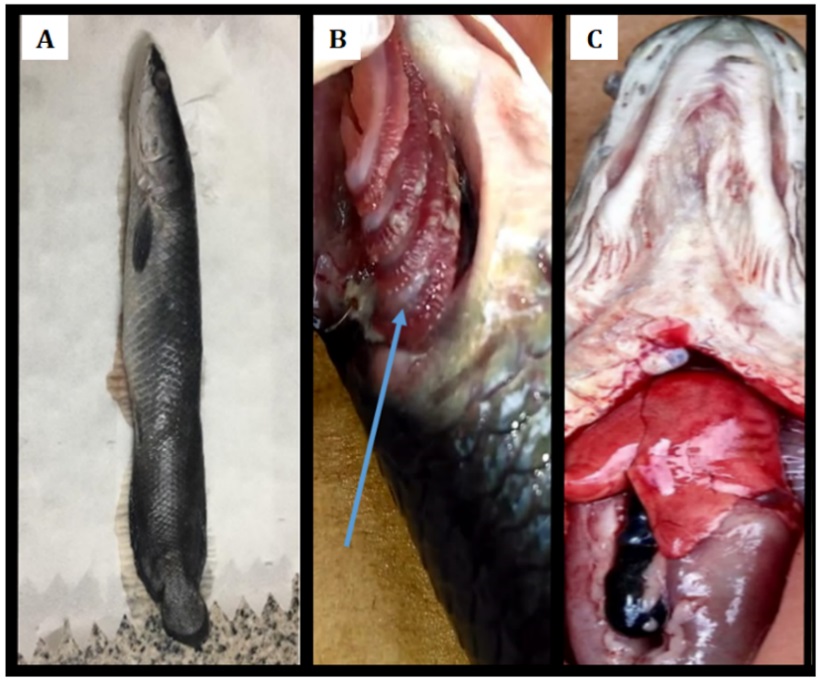
Pirarucu (Arapaima gigas) is one of the most important fish in Amazonian fish farming. However, information about its nutritional, zootechnical and microbiological aspects is still scarce. This is especially true for the juvenile phase due to high mortality rates caused by malnutrition, difficulties in food training, endo and ectoparasite infestations, which in turn lead to immunosuppression, favoring secondary bacterial infections that may be present due to various environmental factors (e.g., sudden temperature variations, water acidity and pollution of the aquatic environment) and the status of fish. The Pseudomonas sp. species studied in this work is part of the aquatic ecosystem and is considered a contaminant or invader because it infects a wide variety of aquatic species, including pirarucu. Given this assumption, the objective of the study was to report a case of Pseudomonas sp. in the viscera and dorsum of a juvenile pirarucu Arapaima gigas (SCHINZ, 1822) detected through bacteriological analysis. In the fish production chain in the Western Amazon, pirarucu is one of the most prominent fish species because of its high zootechnical performance in terms of weight gain and commercial value. However, one of the biggest obstacles in its production chain occurs during the juvenile phase, with high mortality rates caused by mainly bacterial infections, leading to economic losses in fish farming. In this study, Pseudomonas sp. was detected in a sample of dorsum and viscera of a pirarucu fish from a fish farm in the municipality of Ouro Preto do Oeste, Rondônia, Brazil.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Autores que publicam na Acta Veterinaria Brasilica concordam com os seguintes termos: a) Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. b) Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. c) Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).


 Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença
Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença 