Topical treatment of external otitis in cats with combination of levofloxacin, miconazole and dexamethasone
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21708/avb.2019.13.2.8422Resumo
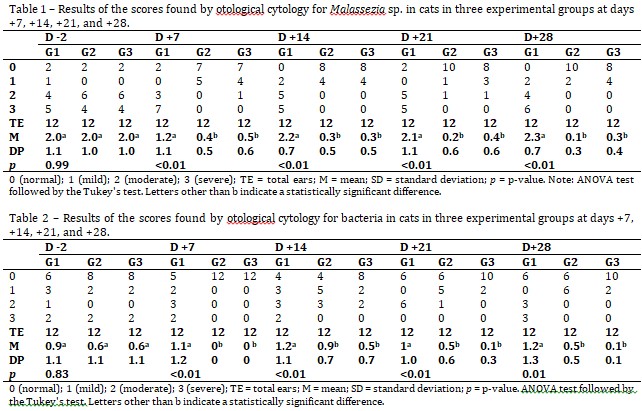
The objective of this work was to evaluate the efficacy of a topical formulation containing levofloxacin, miconazole, and dexamethasone in the treatment of external otitis in cats. Eighteen cats showing clinical signs of external otitis—in the video otoscopy examination and cerumen cytology—were evaluated. The animals were divided into three groups of six animals. Group 1 (G1) was the control group; Group 2 (G2) was treated with a combination of 0.5% levofloxacin, 2% miconazole, and 0.02% dexamethasone, using distilled water as the vehicle; and Group 3 (G3) was treated with the same combination, using vegetable glycerin as the vehicle. The animals were reassessed weekly; animals in G1 had no improvement of clinical signs of otitis or in the findings in the cerumen cytology. However, animals in G2 and G3 showed improvement of clinical signs, and control of yeasts and/or bacteria in the cytological examination of the ear after seven days of treatment. Based on the results, the formulation containing the combination of levofloxacin, miconazole, and dexamethasone was effective in controlling the perpetuating factors of external otitis in cats.
Downloads
Downloads
Publicado
Edição
Seção
Licença
Autores que publicam na Acta Veterinaria Brasilica concordam com os seguintes termos: a) Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. b) Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. c) Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).


 Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença
Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença 