Seminoma and sertolioma in non-cryptorchid dog – case report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21708/avb.2021.15.4.10155Abstract
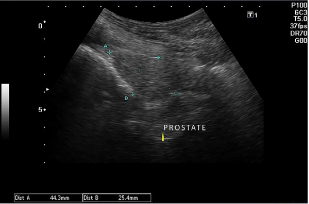
The most common testicular neoplasms in dogs are seminoma, leydigocytoma and sertolioma, affecting middle-aged and elderly dogs, where cryptorchidism is a predisposing factor, as well as some breeds. It can occur alone or, less frenquently, concurrently, generally affecting the same testicle. This study aimed to report the case of a non-cryptorchid 14-year-old mixed breed dog diagnosed with seminoma and sertolioma, each in a testicle. The animal showed an increase in scrotal volume, with no changes in other clinical parameters on physical examination. On ultrasound examination, it was possible to observe alterations suggestive of neoplasia in both testicles and prostatic alteration suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Complementary blood count and biochemical tests were performed and, as treatment, orchiectomy was performed. Fragments were collected from both testicles and sent for histopathological examination. Microscopy of the left testicle showed the presence of round cells, multiple and evident nucleoli, cells in different phases of mitosis and binucleation, these changes being compatible with seminoma. In contrast, in the right testicle, spindle and elongated cells (pseudo-lobular) were observed, presence of long cytoplasmic projections with rounded ovoid nucleus, spindle cells and degeneration of seminiferous tubules, compatible with sertolioma. It was observed that physical examination associated with ultrasound was efficient to detect the presence of neoplasms, being validated by histopathological examination. Orchiectomy was an assertive treatment indicated for this case.
Downloads
Downloads
Pubblicato
Fascicolo
Sezione
Licenza
Autores que publicam na Acta Veterinaria Brasilica concordam com os seguintes termos: a) Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. b) Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. c) Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).


 Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença
Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença 