Urine specific gravity as an indicator for the determination of urinary GGT in dogs with visceral leishmaniasis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21708/avb.2023.17.3.10357Abstract
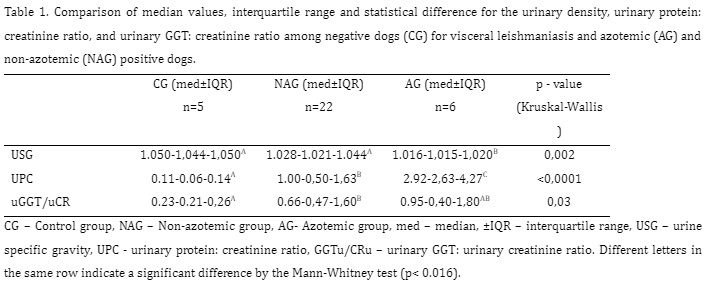
The urinary Gama-Glutamyl Transpeptidase to urinary Creatinine ratio (uGGT/uCR) is a laboratory marker that may signal renal tubular lesion in dogs with visceral leishmaniasis (VL). In this study, our goal was to determine whether urine specific gravity (USG) can accurately indicate an elevated uGGT/uCR and, consequently, tubular injury. Twenty-eight animals with VL and five healthy animals (control group) were included in the study. The diseased animals were classified as azotemic (n = 6) and non-azotemic (n = 22). The difference between all groups was tested with the Kruskal-Wallis test for the USG, uGGT/uCR, and urine protein: creatinine ratio (UPC). Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive value and the accuracy of using USG as an indicator of tubular injury were calculated with the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC curve). The probability of an animal with suboptimal USG presenting tubular injury was obtained by calculating the prevalence ratio. The Kruskal-Wallis test revealed differences between groups for all analyzed parameters (p< 0.05). The chosen USG cut-off value, determined by the ROC curve was 1.030, with an accuracy of 78.09%. The probability of a dog with LV and USG below 1.030 having a high uGGT/uCR ratio was 4.95 (p <0.01, 95% CI - 1.32-18.48) when compared to individuals with ideal DU. In conclusion, dogs positive for Leishmania sp. with low USG (<1.030) should have their uGGT/uCR ratio measured to verify the presence of tubular injury even before the onset of azotemia.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Acta Veterinaria Brasilica

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Autores que publicam na Acta Veterinaria Brasilica concordam com os seguintes termos: a) Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. b) Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. c) Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).


 Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença
Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença 