Isolation of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus in raw milk from refrigeration tanks: identification and antimicrobial resistance profiles
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21708/avb.2022.16.3.10768Abstract
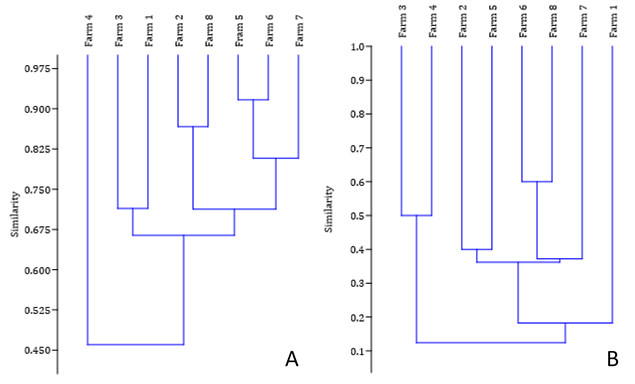
Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus in milk cooling tank reflects a hygienic deficit in animal management, production environment, and milk obtainment. With implications for public health as agents of infection and food poisoning, and the presence of antimicrobial-resistant strains. Therefore, were investigated in cooling tanks with high counts of somatic cells and total bacteria in milk. Microorganisms, in which a profile of resistance to antimicrobials was investigated, and whether there was a similarity in this profile between the strains of the eight dairy properties. Therefore, eighty-eight samples were obtained, and inoculated on Compact Dry® plates. Of this total, 27.27% (24/88) samples tested positive for E. coli and 56.81% (50/88) for S. aureus. Among 24 E. coli strains subjected to disk-diffusion antibiograms, 70.83% were resistant to rifampicin, 50% to ampicillin and 41.67% to cefoxitin and erythromycin, while of the 51 S. aureus strains, 94.32% expressed resistance to azetroanam, 86.27% to ampicillin and nalidixic acid, 76.47% to rifampicin and 47.06 % to erythromycin and cefoxitin. A criterion of resistance to over three antibiotics was observed for 8.33% (2/24) of the isolated E. coli strains and 17.65% (9/51) of the S. aureus strains, characterizing them as multidrug resistant (MDR) strains. Resistance phenotypes displayed high similarity between properties F5 and F6 for S. aureus, and properties F6 and F8 for E. coli when applying the Jaccard index. The presence of these antibiotic-resistant pathogenic microorganisms indicate flaws in milk production handling and sanitary conditions, representing risk to milk consumers.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Acta Veterinaria Brasilica

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Autores que publicam na Acta Veterinaria Brasilica concordam com os seguintes termos: a) Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. b) Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. c) Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).


 Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença
Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença 