Metabolic bone diseases in a wild crab-eating hawk and a caboclo hawk in Paraiba
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21708/avb.2018.12.2.7618Abstract
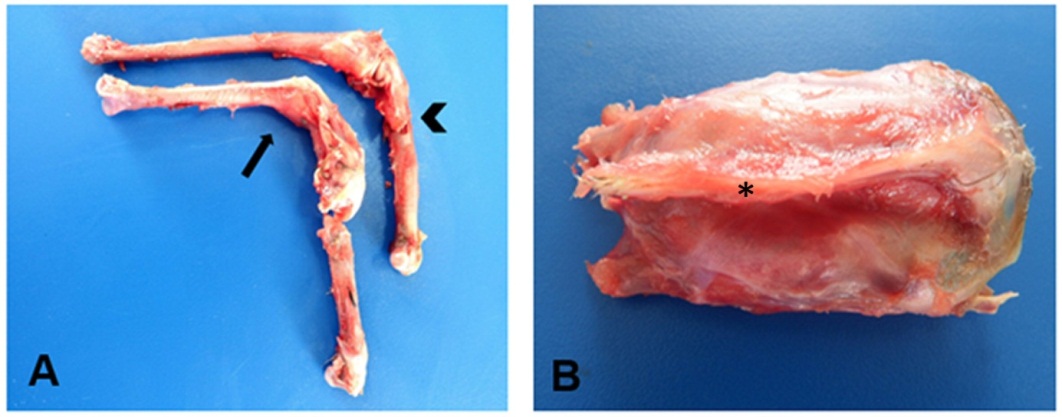
The amount of research on metabolic bone diseases in commercial birds is considerable, however, there is a large gap in the knowledge of these diseases in wild birds. Aspects related to diet are the main factors that cause these diseases, such as: vitamin D deficiency, insufficient calcium intake, or imbalance of calcium and phosphorus in the diet, and problems in the absorption and metabolism of these compounds. This study reports two cases of bone diseases in birds of the order Accipitriformes, which are wild in the state of Paraíba, a crab-eating hawk with rickets, and a caboclo hawk with fibrous osteodystrophy. The diagnosis in both cases was based on macroscopic and microscopic findings. These reports are subsidies for the bird clinic of the order Accipitriformes and for the maintenance of these birds in nurseries and zoos. This study demonstrates the need for further studies to assess whether such cases can be used as indicators of environmental imbalance.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Autores que publicam na Acta Veterinaria Brasilica concordam com os seguintes termos: a) Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. b) Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. c) Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).


 Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença
Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença 