Pulmonary metastasis of transmissible venereal tumour in a dog: a case report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21708/avb.2021.15.3.9809Resumen
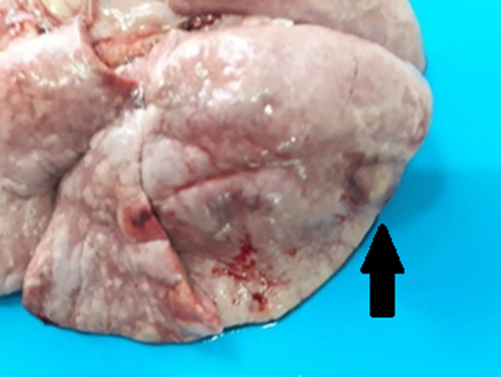
The transmissible venereal tumour (TVT) is one of the most frequent neoplasias in dogs. This tumour has specific characteristics, and it is exclusively of canines. Its transmission occurs through viable neoplastic cell transplantation when in contact with mucosa or unhealthy skin and rarely metastasise. This paper aims to report a rare presentation of pulmonary metastasis of widespread transmissible venereal tumours in a Blue Heeler dog. The patient was cachectic, dyspnoeic, and dehydrated and had multiple skin and pharynx nodulations. The cytology of all cutaneous nodulations showed round vacuolated cells with large eccentric nuclei and loose chromatin, which is compatible with TVT’s microscopic characteristics. Owing to the clinical evolution and reserved prognosis, the patient was euthanized. Necroscopy revealed a mass in the right pulmonary caudal lobe. The mass showed the same histopathologic characteristic of the others: not encapsulated infiltrative neoplastic proliferation of round vacuolated cells. The atypical manifestation of cutaneous metastasis and mainly pulmonary metastasis, in this case, denote the importance of TVT inclusion as a differential in cutaneous neoplasia, even if they show distant organ metastasis. Therefore, it emphasised the importance of cytology and histology in the diagnosis of nodular affections.
Descargas
Descargas
Publicado
Número
Sección
Licencia
Autores que publicam na Acta Veterinaria Brasilica concordam com os seguintes termos: a) Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. b) Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. c) Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).


 Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença
Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença 