Hematological and histopathological changes in medular aplasia resulting from Ehrlichia canis infection in a Border collie dog
DOI :
https://doi.org/10.21708/avb.2021.15.4.10149Résumé
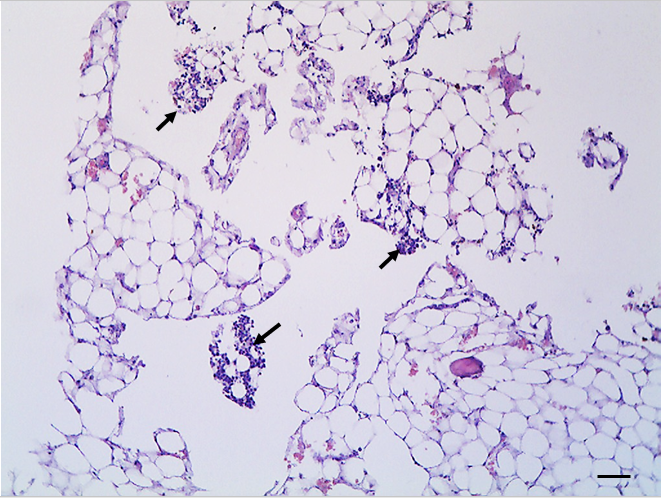
The Canine Monocytic Ehrlichiosis (CME) is an infectious disease that commonly affects dogs of all breeds and ages. It is caused by the bacterium Ehrlichia canis and is transmitted by the tick Rhipicephalus sanguineus. The disease may present itself in the acute, subclinical, and chronic forms. The present study reports the case of a 2-year-old male Border Collie with advanced stage CME, attended at the Pet Clinic of the Veterinary Hospital of the University Federal de Jataí, which resulted in medullary aplasia. The diagnosis of marrow aplasia was based on the necroscopic and histopathological examinations. At necropsy, the diaphyses of the long bones were filled with diffuse, strongly whitish and pasty tissue, typical of the adipose tissue, also found in the femoral epiphyses. The histopathology showed unilocular adipose tissue as the major constituent of the bone marrow and rare islands of marrow cells. These findings were compatible with severe hypoplasia of the red bone marrow and hyperplasia of the white bone marrow, affecting hematopoiesis, resulting in the laboratory alterations observed in the hematocrit, WBC, and plateletogram.
Téléchargements
Téléchargements
Publié-e
Numéro
Rubrique
Licence
Autores que publicam na Acta Veterinaria Brasilica concordam com os seguintes termos: a) Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. b) Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. c) Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).


 Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença
Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença 