Cellulolytic activity of anaerobic facultative fungi from the digestive tract of sheep fed with banana leaf hay
DOI :
https://doi.org/10.21708/avb.2023.17.1.11015Résumé
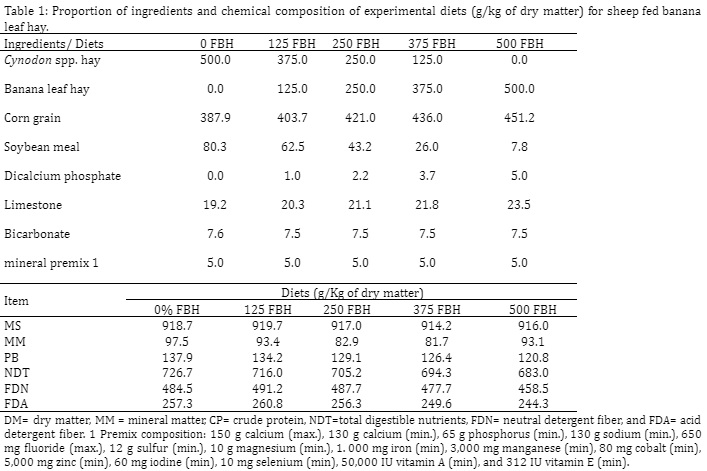
Cellulose degradation is an important process for obtaining energy in the rumen of animals raised with fibrous foods and for the microbiological industry. In this study, the cellulolytic activity index (CAI) of aerobic mycelial fungi from the digestive tract of sheep was evaluated. A total of 30 lambs were raised in an intensive system, distributed in a completely randomized design, with five diets and six replications. Gradual replacements of Cynodon ssp. hay by banana leaf hay were promoted. Approximately 15 mL of ruminal content and swabs from the rectal ampoule were collected. The cultures were carried out in C medium, containing microcrystalline cellulose; and the mycelial fungi isolates were identified after the microculture technique. Among the fungi from rumen fluid, 23 isolates corresponded to the genus Aspergillus and three to Paecilomyces. Seven Aspergillus spp. and three Paecilomyces spp. were identified to samples of rectal ampoule. The Aspergillus genus predominated among the isolates (P <0.05). Fragments of fungus isolates were inoculated in triplicate in medium C at 37°C and the CAI was determined after 24, 48 and 72 hours of incubation. Differences between the CAI of Aspergillus spp. isolates from animals in different diets were not detected (P >0.05). Twenty-two isolates of Aspergillus spp. and three Paecilomyces spp. isolated produced CAI > one, indicating biotechnological potential for cellulase production.
Téléchargements
Téléchargements
Publié-e
Numéro
Rubrique
Licence
(c) Tous droits réservés Acta Veterinaria Brasilica 2023

Cette œuvre est sous licence Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International.
Autores que publicam na Acta Veterinaria Brasilica concordam com os seguintes termos: a) Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. b) Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. c) Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).


 Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença
Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença 