Fungal dermatitis by Scopulariopsis brevicaulis in Guinea pig (Cavia porcellus)
DOI :
https://doi.org/10.21708/avb.2021.15.3.9674Résumé
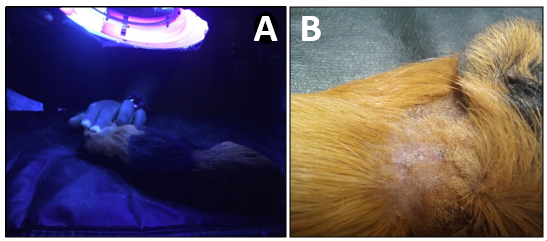
Fungal dermatitis is classified into superficial, cutaneous and subcutaneous mycoses. However, the incidence of fungal dermatitis in small mammals is relatively low. Among rodents guinea pig the most affected specie, however it usually has an asymptomatic pattern. The present text reports an unusual case of fungal dermatitis in Cavia porcellus caused by Scopulariopsis brevicaulis. The animal was received with complaint of alteration of coat around the neck, as well as report of incorrect feeding management. During the physical examination the presence of a dry and crusty dermatitis, negative on fluorescence test of wood. Samples of blood, skin, scabs and hair were collected for parasitic and mycological analysis. The hematological evaluation showed only a discrete eosinophilia; no ectoparasites were observed, but it was noticed the presence of Scopulariopsis brevicaulis. The animal underwent terbinafine and griseofulvin protocol, with total regression of the lesions after 30 days. S. brevicaulis is an unusual geophilic fungus causing animal mycosis, presenting more pathological reports in human mycoses, thus, representing a zoonotic potential. According to the clinical findings and results obtained from mycology assay, it was diagnosed dermatitis by Scopulariopsis brevicaulis, secondary to nutritional deficiency. The combined use of topical terbinafine with systemic griseofulvin was efficient in the treatment. Finally, it was recommended a dietary correction.
Téléchargements
Téléchargements
Publié-e
Numéro
Rubrique
Licence
Autores que publicam na Acta Veterinaria Brasilica concordam com os seguintes termos: a) Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. b) Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. c) Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).


 Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença
Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença 