Thermogenic oils as a substitute for ractopamine in the production of heavy pigs
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21708/avb.2022.16.2.10599Resumo
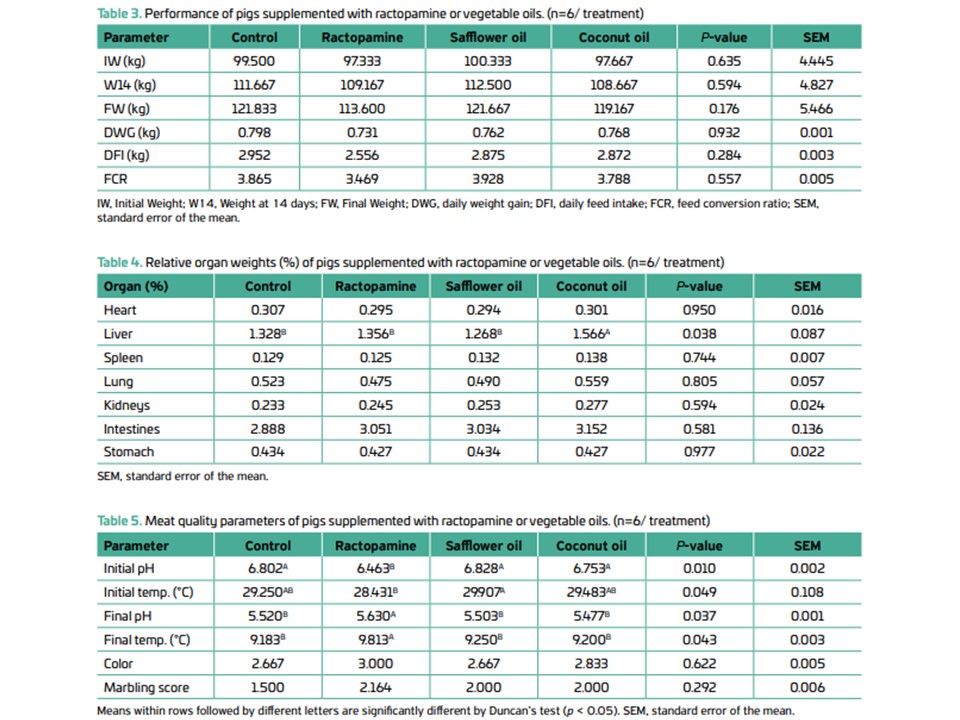
This study aimed to assess the effects of thermogenic oils (safflower and coconut oils) as a replacement for ractopamine in heavy pig diets. A total of 24 mix-breed barrows with an average weight of 98.70 ± 1.63 kg were distributed in a randomized block design with four treatments and six replicates. Treatments were as follows: basal diet, modified basal diet + 10 ppm ractopamine, basal diet + safflower oil, and basal diet + coconut oil. Animal performance, organ weights, meat quality, carcass traits, and economic viability were determined. Data were analyzed using Duncan's test at the 5% significance level. The safflower oil diet resulted in the highest carcass meat and ham weights, whereas the coconut oil diet provided the highest loin eye area and the lowest fat area, resulting in the highest meat/fat ratio. Analysis of economic viability indicators revealed that vegetable oil treatments differed significantly from other treatments in feed cost, feed cost per kilogram of live weight, economic viability index, and cost index, given that oil inclusion increased the price of diets. Supplementation of heavy pig diets with thermogenic oils is a viable alternative to enhance lean meat production, but its use depends on market availability and product price.
Downloads
Downloads
Publicado
Edição
Seção
Licença
Copyright (c) 2022 Acta Veterinaria Brasilica

Este trabalho está licenciado sob uma licença Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Autores que publicam na Acta Veterinaria Brasilica concordam com os seguintes termos: a) Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. b) Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista. c) Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).


 Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença
Esta obra está licenciada com uma Licença 